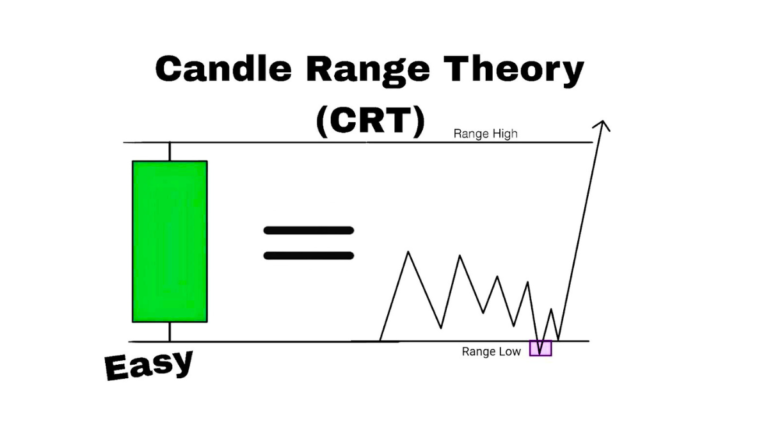
ICT Liquidity Sweep and Liquidity Run
Liquidity is a cornerstone of trading within the ICT (Inner Circle Trader) framework. Understanding the distinction between a liquidity sweep and a liquidity run is essential for effectively employing ICT strategies.
In this blog post, we will explore these two critical liquidity-related concepts and highlight their key differences.
What is Liquidity Sweep?
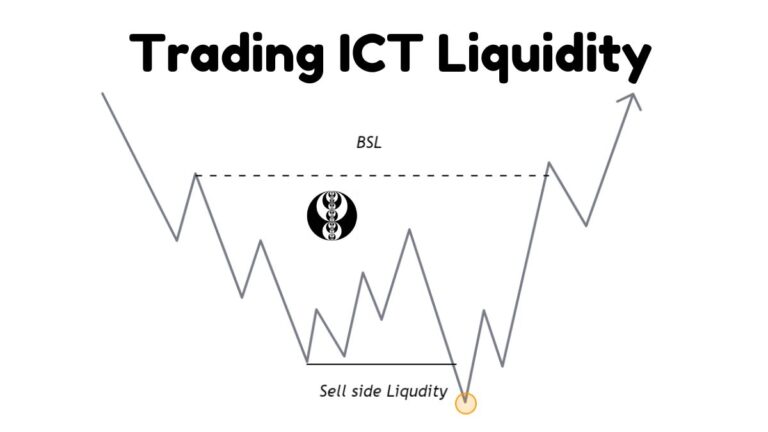
A liquidity sweep, often referred to as a stop hunt, occurs when the market targets and triggers stop-loss orders placed by traders at key support or resistance levels. Market makers or larger players intentionally push the price to these levels to activate the stops, resulting in a temporary spike or dip in the market. This action often reverses the market direction. The primary objective of a liquidity sweep is to generate the necessary liquidity for executing larger positions.
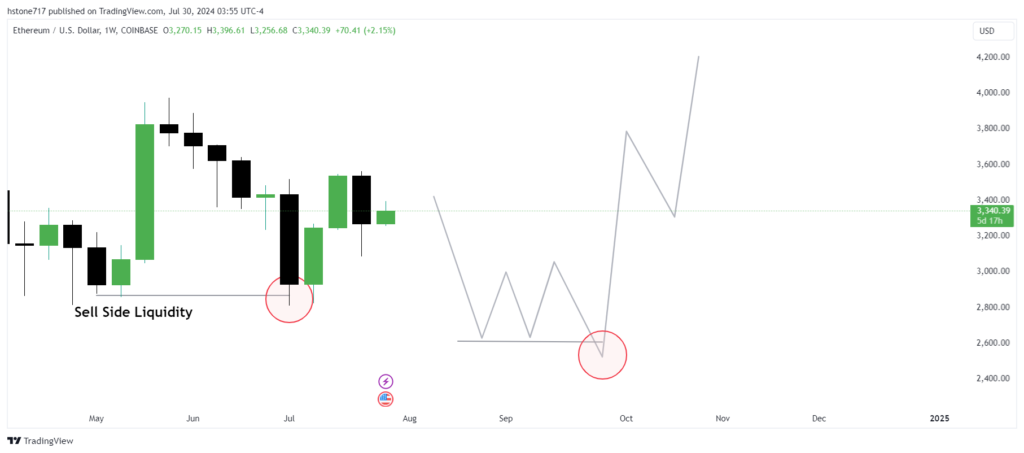
The above ETHUSD chart on weekly time frame explain the liquidity hunt concept. The price level 2876.22 is the key support level and trader place their stops below this level. Price goes down this level 2876.22 and after clearing liquidity moves in opposite direction.
Bullish Liquidity Hunt Example
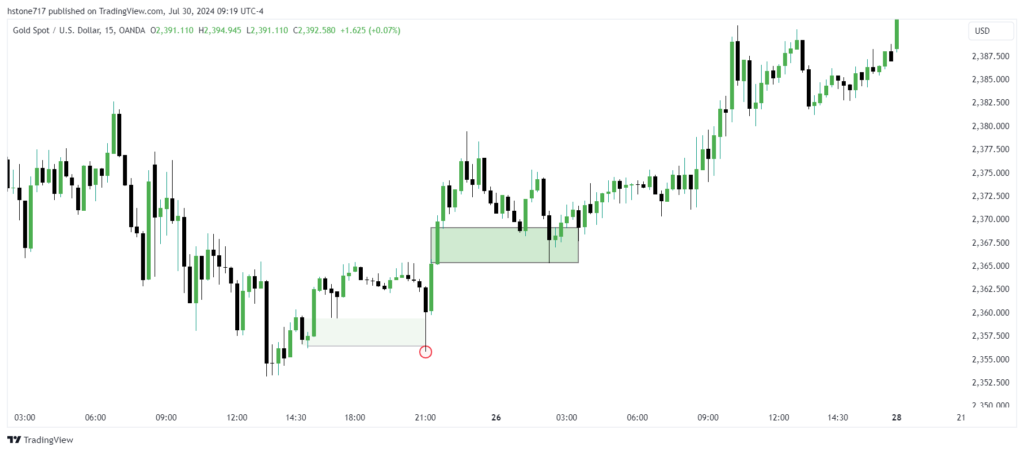
Sure! Here’s a revised version of your statement:
The GOLDUSD chart shows the price sweeping liquidity around the 15-minute bullish order block at the 2365.377 price level. This sweep leaves a price imbalance, also known as a Fair Value Gap. Eventually, the price fills this imbalance and then moves in an upward direction.
Bearish Liquidity Sweep Example
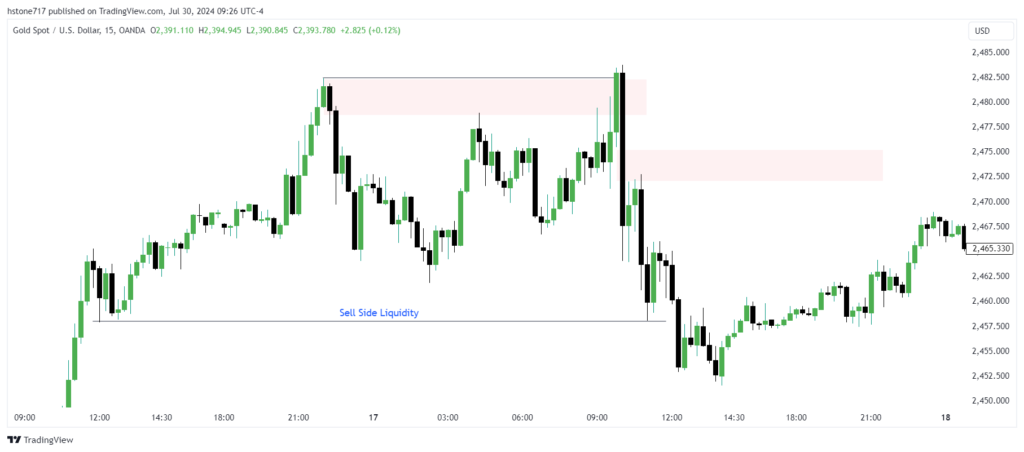
What is Liquidity Run?
An ICT liquidity run occurs when the price moves in the direction of the prevailing trend, targeting liquidity and continuing its movement without reversing direction.
Bullish Market Example:
- In a bullish market, the price targets a previous high, captures the liquidity there, and then continues to rise, reaching a new high.
Bearish Market Example:
- Conversely, in a bearish market, the price targets a previous low, captures the liquidity, and then continues to fall, reaching a new low.
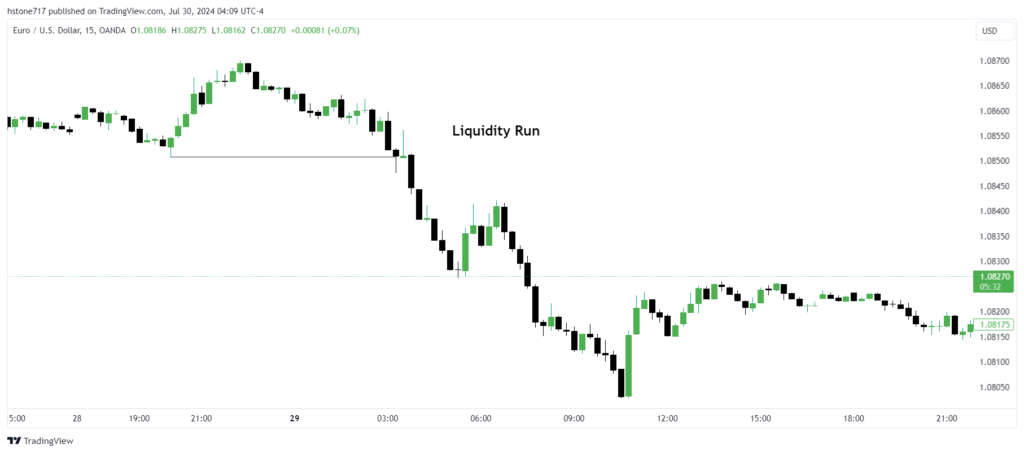
This phenomenon is called a liquidity run because the price captures liquidity and maintains its direction.
Difference Between Liquidity Hunt and Liquidity Run
| Aspect | Liquidity Sweep | Liquidity Run |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | A temporary move in price that takes out stop orders before reversing | A sustained move in price that continues in one direction |
| Purpose | To trigger stop losses and gather liquidity | To continuously drive price in a particular direction |
| Typical Outcome | Price often reverses after sweeping liquidity | Price generally continues moving in the same direction |
| Trader’s Perspective | Seen as a manipulation to gather orders | Seen as a strong trend or movement |
| Example Scenario | Price briefly spikes above a resistance level and then drops | Price consistently rises over a period, breaking multiple resistance levels |